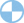
countries with constitutional monarchy
countries with constitutional monarchy 21 Nov countries with constitutional monarchy
[a], These are the approximate categories which present monarchies fall into:[citation needed]. They must be at least 30 years old but, unlike most monarchies, do not necessarily have to be the eldest son of the previous monarch. The list is colour-coded according to the type of government, for example: blue represents a republic with an executive head of state, and red is a constitutional monarchy with a ceremonial head of state. Who was the first constitutional monarchy? A monarchy is a kind of government where the leader of a group, usually a family, inherits leadership by birth and rules a state or a polity for the entirety of his/her life or until abdication. In case a son or daughter is unavailable, then the power goes to the closest blood relation. Napoleon Bonaparte is considered the first monarch proclaiming himself as an embodiment of the nation, rather than as a divinely appointed ruler; this interpretation of monarchy is germane to continental constitutional monarchies. All these states are governed constitutionally with hereditary succession. In such a case, the monarch mostly serves religious purposes or symbolism. [33][34][dubious discuss] The head of state is a constitutional monarch who normally only exercises his or her powers with the consent of the government, the people and/or their representatives (except in emergencies, e.g. Updates? Political scientist Vernon Bogdanor, paraphrasing Thomas Macaulay, has defined a constitutional monarch as "A sovereign who reigns but does not rule".[3]. Democracy - a form of government in which the supreme power is retained by the people, but which is usually exercised indirectly through a system of representation and delegated authority periodically renewed. Collective presidency consisting of three members; one for each major ethnic group. They can amend, reject, or create laws, represent the country's interests abroad, appoint political leaders, and so on. The president is elected by parliament and holds a parliamentary seat, much like a prime minister, but is immune from a vote of no confidence (but not their cabinet), unlike a prime minister. The United Kingdom: The most well-known monarchy in the world The monarchy that the majority of people are most familiar with is that of the United Kingdom. In some cases nations may have multiple ruling bodies or government types, meaning they're not exclusively countries that are governed by constitutional monarchy. Oil giant Saudi Arabia and the small island kingdom of Bahrain are both ruled by kings, while Oman is ruled by a sultan. Stats Category Country profiles and "Which countries are governed by constitutional monarchy?" Andorra Andorra la Vella Andorra, officially the Principality of Andorra, also called the Principality of the Valleys of Andorra, is a sovereign landlocked microstate in Southwestern Europe, located in the eastern Pyrenees .more #67 of 101 The Best Soccer Countries In The World This combination of civil and religious authority can help It became a British protectorate in 1892 and gained its independence in 1978. Other constitutional monarchies include Belgium, Cambodia, Jordan, the Netherlands, Norway, Spain, Sweden, and Thailand. When Papua New Guinea gained independence from Australia, they asked the Queen of England to remain their monarch. Your email address will not be published. The appointed figurehead is called O le Ao o le Malo. The prime minister is the leader of the government. We cite peer reviewed academic articles wherever possible and reference our sources at the end of our articles. In The English Constitution, British political theorist Walter Bagehot identified three main political rights which a constitutional monarch may freely exercise: the right to be consulted, the right to encourage, and the right to warn. The British Monarchy is known as a constitutional monarchy. Encyclopaedia Britannica's editors oversee subject areas in which they have extensive knowledge, whether from years of experience gained by working on that content or via study for an advanced degree. one is elected by common citizens of a foreign country (France), but not by Andorrans as they cannot vote in the French Presidential Elections. For instance, when Hereditary Prince Alois of Liechtenstein threatened to veto a referendum to legalize abortion in 2011, it came as a surprise because the prince had not vetoed any law for over 30 years (in the end, this referendum failed to make it to a vote). Omissions? Along with France, as epitomized by King Louis XIV, absolute monarchs ruled other European countries, including England Spain, Prussia, and Austria. Since 1783, Bahrain has been ruled by the descendants of Khalifa bin Mohammed. a constitutional crisis or a political deadlock). The Convention for the Conservation of Antarctic Seals (1972), 4. One of the popular monarchs is Her Majesty Queen Elizabeth II of United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland. Tuvalu is a remote pacific island nation near Fiji, Vanuatu, and Tonga. There are 38 constitutional monarchies in existence today split into two types: parliamentary and semi-constitutional. Since 1917, the king has had little political power. Two constitutional monarchies Malaysia and Cambodia are elective monarchies, in which the ruler is periodically selected by a small electoral college. Definitions of the major governmental terms are as follows. The figurehead monarch remains to be Queen Elizabeth II, and she appoints the governor-general, who is the head of state. Constitutional - a government by or operating under an authoritative document (constitution) that sets forth the system of fundamental laws and principles that determines the nature, functions, and limits of that government. Rule generally alternates between two branches of the dynasty, although there have been occasional diversions from this pattern due to backroom political deals. A Short History of the World", "Semi presidential systems and semi constitutional monarchies: A historical assessment of executive power-sharing", "Thai King Bhumibol Adulyadej dies at 88", "The Imperial Institution - The Imperial Household Agency", https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Constitutional_monarchy&oldid=1141691922. The monarchy of Canada is Canada's form of government embodied by the Canadian sovereign and head of state.It is at the core of Canada's constitutional federal structure and Westminster-style parliamentary democracy. A combined head of state and head of government in the form of an executive president is either elected by the legislature or by voters after candidates are nominated for the post by the legislature (in the case of Kiribati), and they must maintain the confidence of the legislature to remain in office. Later, Fascist Italy could also be considered a constitutional monarchy, in that there was a king as the titular head of state while actual power was held by Benito Mussolini under a constitution. Other constitutional monarchies include Belgium, Cambodia, Jordan, the Netherlands, Norway, Spain, Sweden, and Thailand. [13] Full parliamentary republican systems that do not have a directly elected head of state usually use either an electoral college or a vote in the legislature to appoint the president. It became a constitutional monarchy in 1966 after breaking from the British Crown. List of countries, nations and states governed or ruled by a constitutional monarchy, sorted alphabetically. It is noteworthy that some scholars in the People's Republic of China claim that the country's system of government is a "semi-presidential system combining party and government in actual operation". Spain has had a long history of controversial monarchs, including the Catholic monarchs such as KingFerdinand II andQueenIsabella I who instituted the Spanish Inquisition. [11][12] Queen Victoria was the last monarch to exercise real personal power, but this diminished over the course of her reign. He appears to still wield more power than most figurehead kings, but has on paper ceded much of his power to the elected bodies. A 2011 referendum, instigated to show reform following the Arab Spring, curtailed the kings power. For instance, the monarch of the United Kingdom can theoretically exercise an absolute veto over legislation by withholding royal assent. Antigua and Barbuda is a single Caribbean nation. In some cases, monarchs are all powerful, that is autocratic, while in some cases they may be ceremonial in that they have no power or have limited power. Among the powers retained by the Thai monarch under the constitution, lse majest protects the image of the monarch and enables him to play a role in politics. [14], Today, the role of the British monarch is by convention effectively ceremonial. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. The monarchs colors, orange, are also the colors of the nation in sporting events. Canada is another country with Queen Elizabeth II as a figurehead monarch. The British monarch is the head of state and is represented by an appointed governor-general. The monarchy today is a ceremonial one, with the prime minister as the head of government. Several states that are constitutional republics are in practice ruled as authoritarian states. The United Kingdom is the most famous example of a country with a constitutional monarchy. For example in 1886 she vetoed Gladstone's choice of Hugh Childers as War Secretary in favour of Sir Henry Campbell-Bannerman. A constitutional monarchy is a monarchy that is ruled by a written constitution. Italics indicate states with limited recognition. Countries governed by constitutional monarchies today include the United Kingdom, Belgium, Norway, Japan, and Thailand. You can rank all of these items, from Holy Roman Empire to Thailand, both of which are examples of monarchy. Most monarchies are constitutional, having largely . However, the 2010s did have some troubles, with the king sacking 3 prime ministers. When he sought the Governor-General's approval of the election, the Governor-General instead dismissed him as Prime Minister. After the Second World War, surviving European monarchies almost invariably adopted some variant of the constitutional monarchy model originally developed in Britain. All maps, graphics, flags, photos and original descriptions 2023 worldatlas.com. The figurehead monarch is Queen Elizabeth II. The British Empire in 1914. Among supporters of constitutional monarchy, however, the event confirmed the monarchy's value as a source of checks and balances against elected politicians who might seek powers in excess of those conferred by the constitution, and ultimately as a safeguard against dictatorship. The council is elected by the parliament, but it is not subject to parliamentary confidence during its fixed term. The emperor is the son of the sun goddess and is considered sacred. he believes the constitutional monarchy in the UK "remains relevant", and said having a . The King or Queen serves as the monarch, but holds little actual power. Britain became a constitutional monarchy under the Whigs. Such a case is known as a coregency. Corrections? The president chooses a prime minister and cabinet from the parliament with approval from the parliament, however only the parliament may remove them from office with a vote of no confidence. Overseas Territory of the UK with limited self-government; parliamentary democracy Bhutan constitutional monarchy Bolivia presidential republic Bosnia and Herzegovina parliamentary republic Botswana parliamentary republic Brazil federal presidential republic British Virgin Islands In some occasions, Roman numerals are used to make a distinction between rulers who share the same name. In Denmark and in Belgium, for example, the monarch formally appoints a representative to preside over the creation of a coalition government following a parliamentary election, while in Norway the King chairs special meetings of the cabinet. [2] [3] Two of these are constitutional monarchies ( Lesotho and Morocco ), in which the sovereign is bound by laws and customs in the exercise of his or her powers, and one is an absolute monarchy ( Eswatini ), in which the sovereign rules without bounds. In effect, "presidents" in this system function the same as prime ministers do in other parliamentary systems. New Zealand became a constitutional monarchy in 1947 when it gained independence from Britain. However, the monarch's power is not absolute. Socialism - a government in which the means of planning, producing, and distributing goods is controlled by a central government that theoretically seeks a more just and equitable distribution of property and labor; in actuality, most socialist governments have ended up being no more than dictatorships over workers by a ruling elite. Malaysia is a federal constitutional monarchy with a Yang di-Pertuan Agong as the figurehead monarch. However, this model of constitutional monarchy was discredited and abolished following Germany's defeat in the First World War.